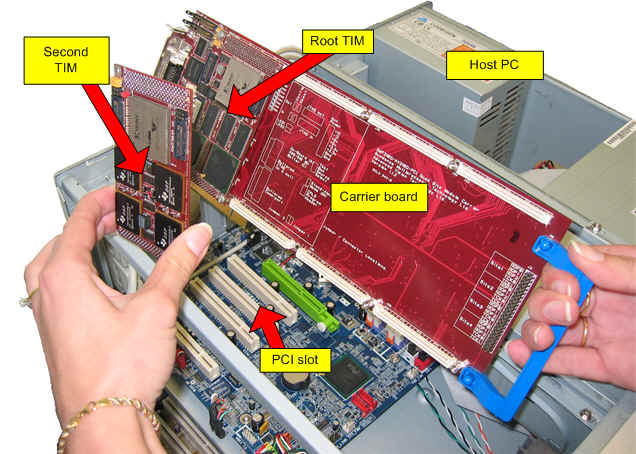
A typical DSP application using Sundance equipment is made up from a host PC holding one or more carrier boards, each supporting one or more processing elements (DSPs, I/O devices, or FPGAs), known as TIMs.

The photo shows a carrier board with one TIM already plugged into a carrier board, and second TIM about to be attached. The carrier boards do not run any programs, they simply hold the TIMs, providing them with power and a means of communicating with the rest of the world. A carrier board plugs into a host PC using a PCI slot.
During development you will use a number of programs on the host PC to develop code for both the DSP and the host PC. You also use the PC to debug your code running on the DSP.